What are dividends and how do they work?
A dividend is a payout of a portion of the profit to the shareholders. The purpose of paying dividends is to attract investors. Dividend can therefore be considered a reward for people who hold the shares for a longer period of time. On this page, you can read how the payout of dividends works.
What is a dividend?
Publicly traded companies may decide to pay out a portion of the profit to the shareholders. Companies are never obligated to pay out dividends.
Some companies never pay out dividends and choose to reinvest the profits instead. As a shareholder, you can still make money by profiting from a rising stock price.
How does the payout of dividends work?
The payout of dividends always goes through a few steps: the announcement, the ex-dividend date, the record date, and the payout date.
Announcement
When a company pays out dividends, an announcement is made first. The announcement indicates how much dividend will be issued and on which date.
The price of a share will then rise by the value of the announced dividend. When a share is traded at $ 10 and $ 1 dividend is paid out, you will see that the price of the share will rise by $ 1.
Ex-dividend date
Another important date is the ex-dividend date. The ex-dividend date is the moment when it is determined who is entitled to dividends. All people who own shares in the company at the time of ex-dividend receive the dividend. You are not entitled to dividends if you buy the share on or after the ex-dividend date.
On the ex-dividend date, the price will drop by the value of the dividend. The share is worth less thereafter, as you are not entitled to the announced dividend. When a share is traded at $ 10 and the dividend is $ 1, the price of the share will drop to $ 9.
Record date
The record date is the date on which the company determines who is entitled to dividends. Shares are freely tradable and constantly change owners. Therefore, the company must determine who is entitled to a portion of the profit. The record date usually takes place one day after the ex-dividend date.
If you want to be entitled to the dividend, you will need to buy the share at least two days before the record date.
Payout date
On the payout date, the shareholders who were entitled to the dividend receive their payout. If you purchased the share on or after the ex-dividend date, you are not entitled to the dividend. The payout date may take place a month later.
It can be interesting to keep an eye on the share price on the payout date. When investors fear that the company cannot really continue without the money, the share price may drop.
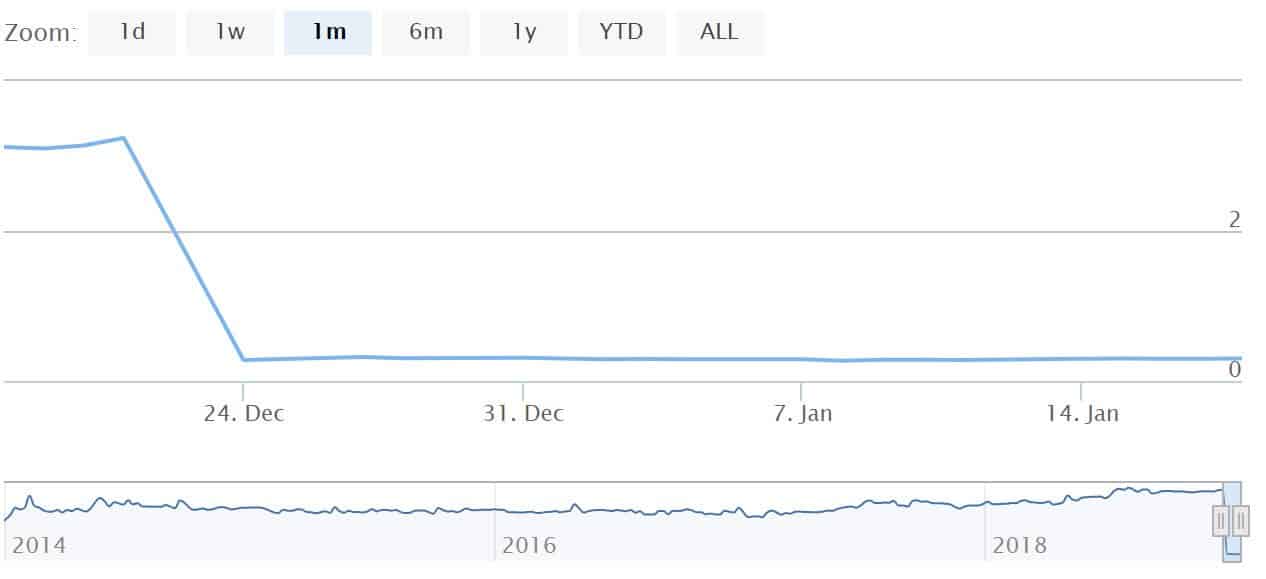
With the HeadFirst Source G share, a dividend of 3 euros was paid out. On the ex-dividend date (December 24), the share opened 3 euros lower.
What types of dividends exist?
- Cash dividend: You receive the dividend in currency in your account.
- Stock dividend: You receive the dividend in shares.
What is a cash dividend?
Cash dividend is the most common form of dividend. The company pays out a portion of its profits in cash.
If you own 1000 shares with a value of $10 per share, then you have a total of $10,000 in share value. If the dividend percentage is 5%, you will receive $500 in cash dividends.
What is a stock dividend?
Occasionally, a company may choose to pay out a portion of its profits in the form of shares. This is also called a stock dividend. Let’s look at an example of how this works.
If you own 1000 shares with a value of $10 per share, then you have a total of $10,000 in share value. If the dividend percentage is 5%, you will receive $500 in stock dividend. With a share price of $10 per share, this means you will receive 50 new shares.
Stock dividend can be advantageous for a company as it helps them maintain liquid assets within the company. However, it can be difficult for shareholders to sell their shares if the company performs poorly.
Why do companies pay dividends?
1. Reward for trust
Shareholders are co-owners of the company. As a reward for this ownership, a company may decide to pay out a portion of its profits in the form of dividends. This allows them to reward loyal shareholders for their trust.
2. Lack of interesting alternatives
A company can often generate more profits in the future by using the income to start new projects. When a company does not see any useful alternative projects, it may choose to distribute the profits to shareholders.
3. Avoiding fear
When a company consistently pays out dividends, lowering this amount can lead to fear. When the dividend is lowered, investors may sell their shares, which causes a decline in share price. This happened, for example, when Shell lowered its dividend for the first time since World War II during the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020.
When a company lowers or even eliminates its dividends, this does not have to be a bad sign. The company may also have an interesting new project in mind that can generate even more profits in the future. It is therefore important to investigate the reason for a dividend cut.
4. Preventing the sale of stocks
Investors may be less likely to sell a stock that pays out a stable dividend, which can keep the stock price steady.

When do companies pay dividends?
1. No fixed policy
When there is no fixed dividend policy, management can decide whether and when to pay dividends. In this situation, there is less certainty for the shareholder. Shares with a variable dividend policy may be more volatile than shares with a more certain dividend policy.
2. Dividend as a fixed percentage of profit
In some stocks, a fixed percentage of profit is paid out as a dividend. With this method, there is a risk that the company will pay out more dividends than is prudent.
3. Fixed or growing dividend
With a fixed dividend policy, the shareholder receives a fixed amount with each payout. In a growing company, this amount increases each period. This is risky because it is not certain that the company will always be able to meet this expectation. If the company suddenly decides to pay out less dividend, the stock price can drop sharply.
The risks of dividend payouts
1. Examine the payout ratio
Do not focus solely on the dividend. When companies pay dividends, it can weaken the position of the company. Therefore, research with, for example, the payout ratio whether the company can safely pay the dividend.
It is also important to pay attention to how the company pays out dividends. Sometimes, companies issue new shares to pay out dividends. However, this dilutes your stake in the company and can reduce the return on your investment in the future.
3. Limit growth
Dividend payouts can also limit growth opportunities. The company then has less money available, which may cause the company to perform less well than its competitors in the future.
Stock buybacks as an alternative
An alternative to paying dividends are stock buybacks. Some companies use their profits to buy back shares. This increases the earnings per share, which gives you as a shareholder a favourable position.
What types of companies pay high dividends?
Not all companies pay high dividends. Companies that have been around for a while and achieve large, predictable profits are more likely to pay dividends. Examples of these types of companies are:
- Oil and gas companies
- Banks and financial institutions
- Pharmaceutical companies
- Utility companies
New startups and rapidly growing companies often pay little or no dividend. These companies normally face high costs or even losses. Examples are companies like Uber or Google. These types of companies prefer to invest their money in new developments and expect to create more value for shareholders in the future.
As a shareholder, you benefit from stocks in two ways: through dividends and through price increases. When a company reinvests its profits, this can benefit the profitability and price of the company.

Utility companies often pay higher dividend percentages
Do you pay taxes on dividends?
In the Netherlands, you pay 15% tax on distributed dividends. This amount is automatically withheld before the company pays the dividend.
Other countries have different dividend percentages. You can avoid double taxation within your tax return by declaring all dividends paid out.
Investing for dividends
Despite a decrease in share price, it is possible to achieve a positive return on stocks with dividends. Especially when you hold on to stocks for several years, dividends can contribute to a positive and steady return.
Dividend investing is often a fairly stable, less risky method of investing. This is because many companies that pay dividends do so on a stable basis. When you focus on stable dividend payments, the stock price development is less important.
An example of a stable stock that has been paying dividends for years is Shell. By investing in stocks with a fixed dividend payment, you can build an income from your stocks.
Reinvesting dividends
Many investors use dividends as extra income: for example, they use it to book a well-deserved holiday. However, by reinvesting dividends in the long term, you can achieve much better investment results. This is due to the effect of exponential growth. None other than Einstein called compound interest the eighth wonder of the world.
When you keep reinvesting the dividend, you also receive a return on that amount. This is also called interest on interest. In the long term, this can add up significantly. In this example, we invest $10,000 each year with an average return of 8%.
- In 10 years, we invest $100,000 and have $156,000 (X1.5).
- In 30 years, we invest $300,000 and have $1,223,458 (X4).
- In 50 years, we invest $500,000 and have $6,196,679 (X12).
Click here to use our compounding tool: this allows you to calculate your capital growth based on the dividend payments.
How to calculate dividend yield?
You can easily calculate the dividend yield on a share. You can divide the total market capitalization (which is the value of all outstanding shares) by the total dividend.
Another way to calculate the dividend yield is by dividing the dividend per share by the price of a share. For example, if a share costs $10 and the dividend yield is $1, you receive a dividend yield of ten percent.
Payout ratio
Dividend yield alone does not tell the entire story. It is also wise to look at the payout ratio. You do this by dividing the total return by the profit. By doing so, you can see how much of the profit the company pays out in dividends.
Free cash flow
You can also investigate the proportion of free cash flow that is paid out as dividends. Free cash flow is the cash that comes in, and the company can spend. You calculate this ratio by dividing the total dividend paid out by the free cash flow.
These formulas can help you determine the safety of the dividend payout. When companies take big risks to keep shareholders happy, it can have a negative long-term effect on the company’s results.
Psychology and dividend
Dividend can have a strong influence on the psychology of any investor. When you constantly receive a steady dividend payout, it can strengthen your confidence in the company. Moreover, dividends provide a protection against inflation.
However, it is important to remember that high dividend payouts can block future dividend growth. After a dividend payout, there is less money available for growth and innovation, which can limit the company’s expansion.

How do you know when a company pays dividends?
Companies usually announce clearly when they pay dividends. Online brokers can then present this data clearly. There are also handy online calendars where you can view all the dates on which dividends are paid out.
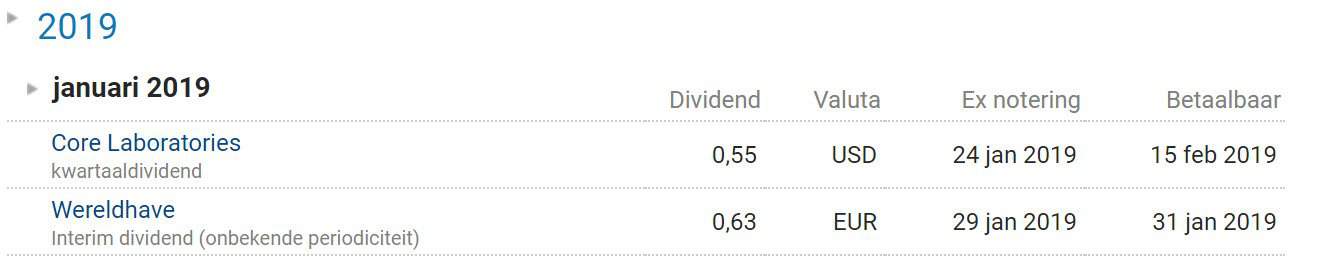
Within the dividend calendar, you can see clearly when dividends are paid out.
What is an interim dividend?
Most companies only pay dividends once a year, but there are also companies that pay out interim dividends. Interim dividends, are a portion of the final dividend to be determined over the fiscal year. At the end of the year, the remaining amount of the dividend to be paid out is determined. Companies may decide to pay dividends every six months or even every quarter.
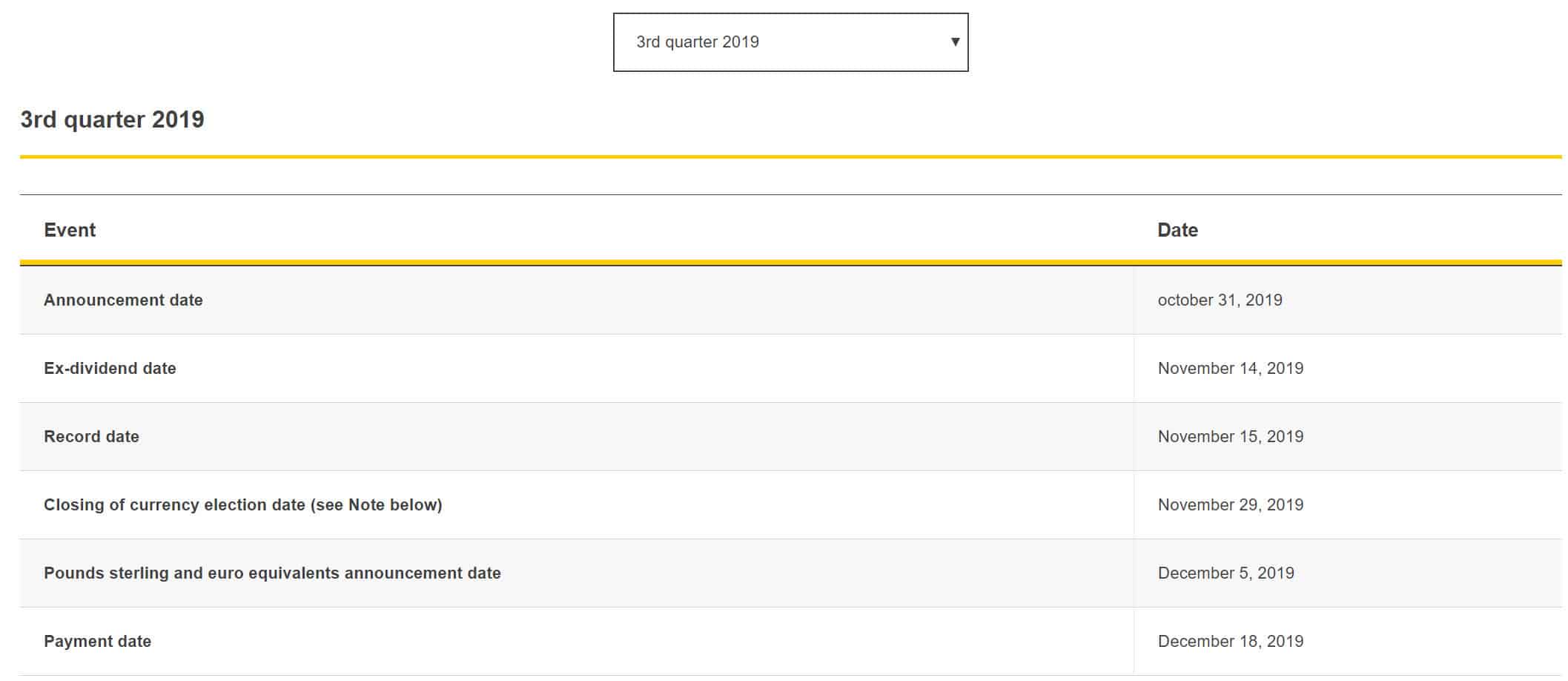
On Shell’s website, you can find the interim dividend by period
Frequently Asked Questions
Dividends originated in the Netherlands. The stock exchange originated in the Netherlands, which happened in 1602 with the founding of the Dutch East India Company.
The Dutch East India Company needed large amounts of money to carry out costly expeditions. They offered investors shares in exchange, which promised a profit distribution. They paid out over 18% of the value of the shares.
There are special situations where dividends can also play a role. For example, a company may decide to sell part of the company. The received acquisition price is then paid out to the shareholders. Depending on what is decided, the shareholders receive a payout in cash dividend or stock dividend.
Companies must comply with certain rules when they want to pay out dividends. Dividends are intended as a profit distribution. Therefore, it is only allowed to pay out dividends from profits or from profit reserves. A company cannot pay dividends from the company’s compulsory legal reserves or from its capital.
Under certain conditions, it may be allowed to borrow money to pay out dividends. This is possible when there are sufficient reserves, but insufficient liquid assets. In this case, you should be careful. The company will have to pay financing costs, which can lower the profitability of the company.
The shareholders have the decisive authority in determining the dividend. Therefore, at the shareholders’ meeting, you can vote on the dividend policy.
Many larger companies that see their stock rise significantly every year see no reason to pay dividends. These companies can still yield a higher return than a stock that pays a steady dividend, but where the stock does not increase considerably in value.
Companies that regularly pay dividends may also decide to skip a payout. For example, they may decide to use (part of) the dividend for new investments or for an acquisition. Eventually, this can lead to an even higher profit distribution.
The amount that you as a shareholder receive in dividends also depends on the type of share: different dividend percentages may apply for priority shares or preferred shares.
Investment funds can also distribute dividends. When you invest in a fund or ETF, you own a participation. This participation gives you ownership over a fraction of the fund’s investments. The fund invests the money of all participants in baskets of stocks and bonds.
Some funds then pay interest on bonds and dividends on stocks to those who own a participation in the fund. This amount is then paid out in the form of a dividend.
Other funds may choose to reinvest the dividend automatically. Click here to discover which funds invest in companies that pay a high dividend.
There is no fixed period in which you have to own stocks to receive a dividend. However, you must own the stocks on the ex-dividend date. At this time, it is determined who is eligible for a dividend payment.
You are eligible for a dividend if you are a shareholder and the company decides to distribute dividends. It is important, however, that you own the stocks on the ex-dividend date.
Author

About
When I was 16, I secretly bought my first stock. Since that ‘proud moment’ I have been managing trading.info for over 10 years. It is my goal to educate people about financial freedom. After my studies business administration and psychology, I decided to put all my time in developing this website. Since I love to travel, I work from all over the world. Click here to read more about trading.info! Don’t hesitate to leave a comment under this article.
