The effect of interest rates on the stock market
Where many savers rejoice at a high-interest rate, a high-interest rate is rarely a reason for celebration for investors. When Central Banks announce an interest increase, stock prices immediately drop. In this article, you can read how changing interest rates affect the stock market.
What are the effects of interest rates on the stock market?
- An increase in interest rates makes borrowing money pricier.
- Companies and consumers therefore spend less money.
- As a result, the profitability of companies decreases.
- Share prices will fall with a higher interest rate.
- Many investors switch from stocks to bonds.
Why do interest rates rise and fall?
Central Banks raise or lower interest rates in a certain economic zone. In America, the Federal Reserve determines the interest rate and in Europe, the European Central Bank does.
The goal of Central Banks is to maintain price stability. This means that prices should not rise too quickly; price increases are also called inflation.
This is the general policy of the Central Bank:
- In cases of too high inflation, the bank will raise interest rates.
- In cases of too low inflation, the bank will lower interest rates.
The effects of an interest rate increase or decrease are often immediately visible on the stock market. The actual effects on the economy are typically not seen until a year later.
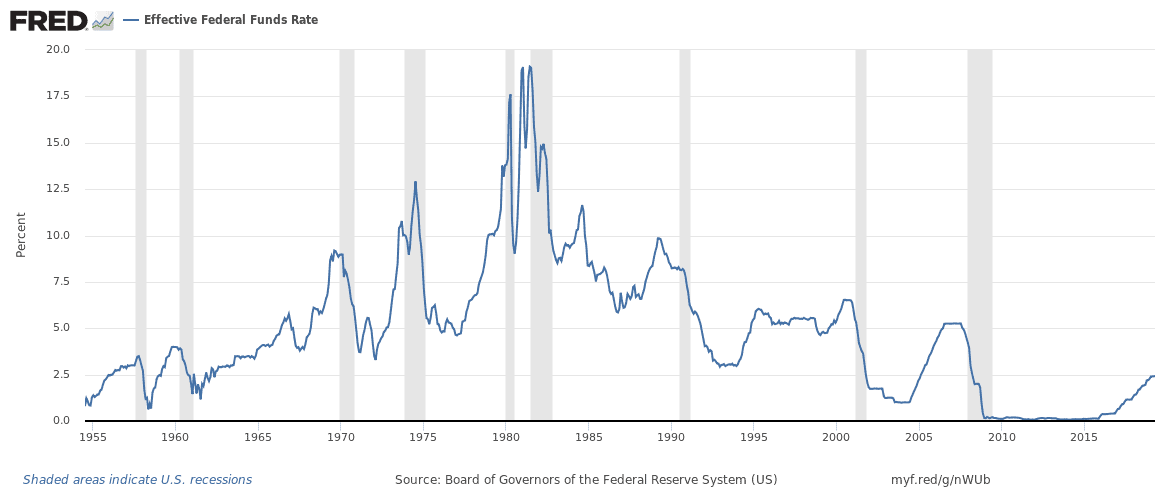
In the above graph, you can see the interest rate that the Fed has established over time
When interest rates rise, borrowing money becomes more expensive
When interest rates rise, both consumers and companies have less access to cheap money. Almost all companies borrow money at some point, either to invest or to achieve a higher profit. Consumers also regularly borrow money to make purchases.
Effect 1: Companies invest less
Large companies regularly borrow money: they do this because they believe that they can make a profit on the credit. When a company pays five percent on loans and earns a return of seven percent, this means that every borrowed dollar makes them money.
However, when interest rates rise, this margin decreases. Companies then borrow less money, causing investments to decline. As a result, the profitability of the company may decrease.
Investments decrease with a higher interest rate
Impact 2: Decrease in company profits
A rising interest rate not only affects a company’s future investments, it can also lead to current financing becoming pricier. When a company suddenly faces higher interest expenses, the company’s profitability can immediately come under pressure.
When earnings per share decrease, shareholders are more likely to sell their stocks, causing the share price to drop.
Impact 3: Investors and borrowed money
Many investors use borrowed money in their portfolios: they use leverage. When investors apply leverage, they invest on margin. The investor must pay interest on the borrowed money.
When interest rates rise, the costs of using margin increase. This makes investing with leverage less attractive. When interest rates rise significantly, investors may even decide to sell their stocks in panic which can lead to a sharp decline in stock prices.
Decline in overall consumption
We briefly discussed in the previous paragraph that companies will invest less when interest rates rise. Money is needed for large expansions and innovations. When interest on these investments increases, companies will postpone or cancel less essential investments.
Decrease in employment
A direct consequence of the decline in the number of investments is that companies spend less money. When companies invest less, employment decreases. There will be fewer projects that require people. Lower employment leads to less spending. The decrease in spending leads to a decrease in sales. This further reduces the profitability of the corporate sector, causing stock prices to fall further.
More expensive consumer credit
At the same time, consumers will spend less because they can no longer purchase consumer goods on credit. This also causes spending to decrease. Companies will sell less as a result, which in turn will make them perform worse which can also lead to a decline in stock prices.
Investors seek alternatives
Investors are constantly looking for the investment product that will yield the highest return. When interest rates rise, the return on savings accounts and bonds increases.
Stocks have always had a riskier image as investment products. Investors want to be adequately compensated for this risk. When bonds or even the average savings account become more attractive, more and more investors will sell their stocks. This can further lower stock prices.
What can you do when interest rates rise?
Option 1: Sell some of your stocks
When interest rates rise, stock prices often fall. At the same time, the return on savings accounts and bonds increases. It may be wise to withdraw some of your money from the stock market and opt for one of these less risky options.
Option 2: Speculate on falling prices
You can also choose to speculate on falling prices by opening a short position on a stock.
Option 3: Look for undervalued stocks
You can also look for bargains. The higher interest rate does not have to be permanent and in the future, companies may perform better. If you want to buy stocks, it is important to research whether the company does not have considerable debts that they are now paying much higher interest rates on.
How can interest rates predict recessions?
It is also possible to use interest rates to predict a future recession. Normally, interest on short-term loan rates are lower than on long-term loan rates. Inflation causes the profitability for the lender to decrease over a longer period of time, since inflation makes the same amount of money less valuable in the future. The lender will then receive a smaller amount in real value. However, there may be a reverse yield curve.
A reverse yield curve is a situation where short-term interest rates are actually higher than long-term interest rates. In the past, this was an indication of the start of a new recession. There is then less confidence in the future. When this happens, it may be attractive to invest in bonds with short maturity. The interest rates on these bonds will be higher. In this situation, it is better to leave stocks alone.
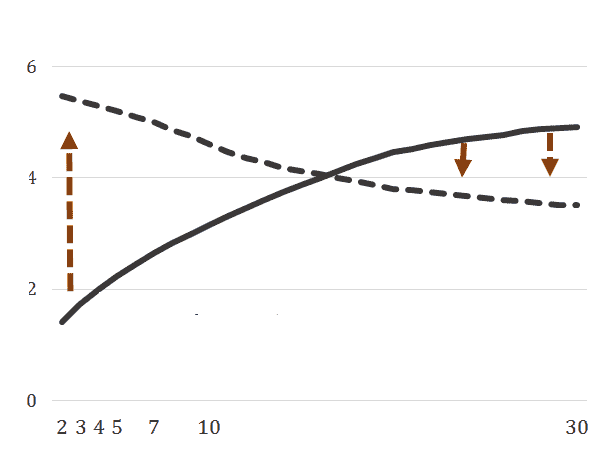
Examine the real interest rate
It is important to pay attention to the real interest rate when analysing the market situation. How much the real interest rate increases depends on inflation. Inflation is the extent to which the average price level rises. When inflation increases, the value of the same amount of money decreases. With higher inflation, the real interest rate increases less. An increase in interest rates of 1% with an inflation of 1% is stronger than an increase in interest rates of 1% with an inflation of 3%.
A higher interest rate does not necessarily have to be bad for the stock market. When the economy performs well, the interest rate can rise somewhat without it having a negative impact on the economy.
What is the effect of a high-interest rate on bonds?
The price of the same bond decreases when the interest rate rises. A bond with a fixed interest payout of 2% is more attractive when savings account interest rates are 1% than when they are 3%.
However, the interest rate on new bonds will be higher. If you think that the interest rate will decrease in the future, it may be interesting to buy bonds.
Real estate & interest rates
When interest rates rise, investing in real estate may become less attractive. With a higher interest rate, you will have to pay more for your mortgage. At the same time, fewer people will be able to take out a mortgage. The prices of houses are largely determined by the available financing space.
The effects of an interest rate increase or decrease are often immediately visible on the stock market. The actual effects on the economy are typically only seen a year later.
Does a higher interest rate always lead to falling prices?
The prices of shares are determined by the interplay of supply and demand. The expectations of millions of investors determine how stock prices develop.
When the majority expects the Fed to cut interest rates by 0.5 percent, but they only cut it by 0.25%, stock prices can still fall. People already bought the stocks based on that expectation, but are then disappointed by the smaller decline and therefore decide to sell their shares.
The following rule applies:
- If the expectation is met: then there is little change in the stock price.
- If the interest rate movement is stronger: then stock prices can fall significantly with a rising interest rate and rise significantly with a declining interest rate.
Therefore, it is always important to keep an eye on sentiment when you start investing in stocks.
Frequently asked questions about interest & stocks
When interest rates are low, you see that companies that pay many dividends often benefit the most: think of companies like Shell. Companies that have to finance a lot of their activities with borrowed money also benefit from low-interest rates: think of real estate companies.
Some stocks perform especially well when interest rates rise. These are typically stocks in the financial sector. For example, banks can charge higher interest rates for lending money.
Growth stocks are strongly affected by high-interest rates. You will find many growth stocks in the technology sector. These stocks typically have high valuations based on future growth. It is difficult to achieve this growth with high-interest rates. In addition, these companies have a lot of debt, which further increases costs.
Auteur

Over Alex Mostert
When I was 16, I secretly bought my first stock. Since that ‘proud moment’ I have been managing trading.info for over 10 years. It is my goal to educate people about financial freedom. After my studies business administration and psychology, I decided to put all my time in developing this website. Since I love to travel, I work from all over the world. Click here to read more about trading.info! Don’t hesitate to leave a comment under this article.
