Explanation of Stock Orders: Market & Limit Order.
When you start investing with a broker, you can choose from different types of orders. In this article, I explain in simple terms how the different order types work.
What types of orders exist?
When buying and selling stocks, you pick a type of order. There are different types of orders, the most important ones are:
- Market order: you buy or sell the stocks directly at the prevailing price.
- Limit order: you buy or sell the stocks at a set price.
- Stop order: you close an open position at a fixed price.
You also always decide between a buy or sell order. With a buy order, you buy the stock and with a sell order, you sell the stock.
What is a market order?
A market order can be seen as a direct order. The broker will try to open the order as quickly as possible at the prevailing price. With a market order, you always know that the shares will actually be bought.
The biggest disadvantage of a market order is that the price at which you buy the stock is uncertain. Especially in very volatile markets, the price of a stock can fluctuate significantly. As a result, the price you pay for a stock with a market order may end up being higher.
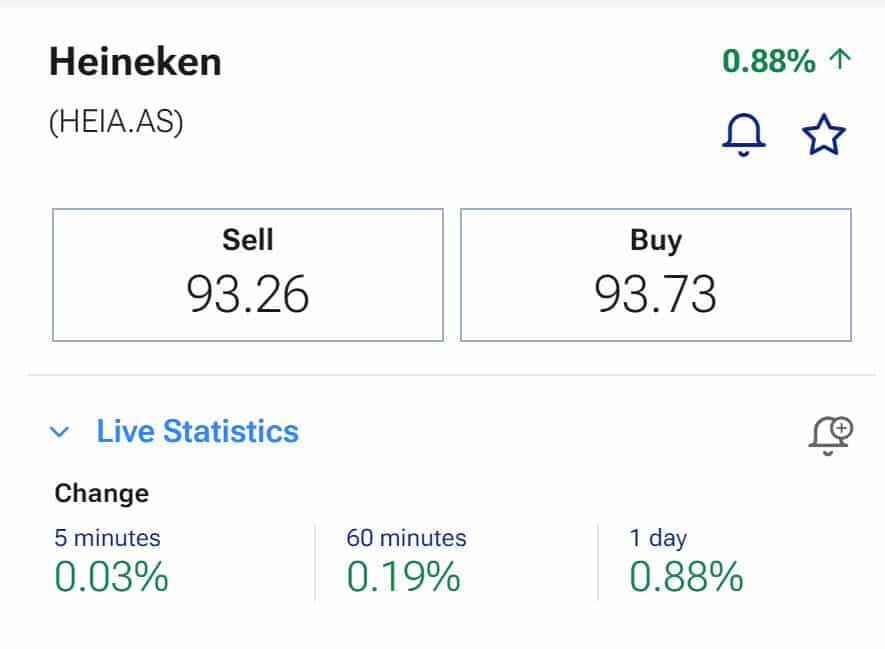
With a market order, you only need to fill in how many shares you want to buy.
What is a limit order?
A limit order is an order that is only executed when a certain price is reached. By setting a limit order at a low value (buy) or a high value (sell), you can strategically and completely automatically open positions.
A big advantage of the limit order is that you have more control over the price at which your investment position is opened. A disadvantage of the limit order is that you are not sure if the investment will be opened. If the price is not available, your investment will not be opened.
For example, you can set that you want to buy a share for $5. In this case, you will never pay more than $5, but possibly less.
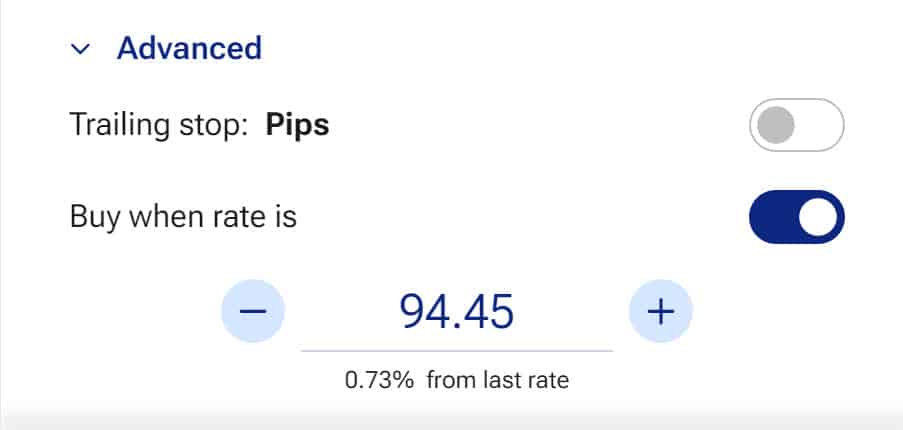 With a limit order, you enter the limit; this is the amount at which you want to buy or sell a share.
With a limit order, you enter the limit; this is the amount at which you want to buy or sell a share.
What types of limit orders are there?
- Buy limit: the stock is bought at a certain price (or cheaper).
- Sell limit: the stock is sold at a certain price (or more expensive).
- Buy stop: a level at which a market or limit order is placed. (buy).
- Sell stop: a level at which a market or limit order is placed to sell.
Long or short order
You can choose to place a long or short order. With a long order, you speculate on an increase in the price, while with a short order, you speculate on a fall in the price. This way, you can speculate on good and bad news.
Would you like to read more about how opening short orders works? Then read this extensive article!
Stop loss/take profit order
It is also possible to place a stop loss or take profit order. The position will be automatically closed at a certain value. It is always advisable to place a stop loss: this allows you to determine the maximum loss. Sometimes it can also be attractive to use a take profit. With a take profit, you can close the position at a certain value where the price often reverses.
By tactically determining when to take profits and losses, you can optimize the profits on your Forex account. It is always advisable to think about an exit strategy before opening a position: this prevents your decisions to be influenced by your emotions.
What is a trailing stop?
A trailing stop can be very interesting when you expect a rise followed by an almost immediate correction. A trailing stop is a moving stop loss. With a trailing stop, you determine an amount of decline at which the position should be closed. However, this value moves along with the price.
When you have opened a long position, and the price rises, the trailing stop also moves up. This way, you can maximize your profits and take advantage of the full rise! Be careful not to set the trailing stop too tight. If you do, the position may be closed too early, while the rise has yet to begin.
Protect your investment with a stop-loss order
With a stop-loss order, you can set a price at which you automatically sell a share. When the stop-loss order level is reached, it is immediately converted to a stop market order. For example, you can set a stop-loss order at $5. When the share falls below $5, it is immediately sold at the best available price.
If you want more control, you can use a stop-limit order. Here too, the stop-limit order is only activated when the share price falls below a certain price. For example, you can set the stop-limit order at $5. When the price is less than $5, the share will only be sold if it can be sold for $5 or more. The risk of a stop-limit order is that your shares may not be sold at all.
Other types of orders for investments
All or None (AON) order
This type of order is only executed when all shares can be purchased. If you want to buy 1000 shares at a price of $5 and there are only 500 available, the order will not be filled.
Immediate or Cancel (IOC) order
When the order cannot be executed within a few seconds, it is automatically removed.
Fill or Kill (FOK) order
This type of order combines AON and IOC. The order is executed only when the specified number of shares can be bought or sold within a few seconds.
Take Profit order
With a Take Profit order, you can automatically take your profit at a certain level. The Take Profit order works the same as the Stop Limit order, but the outcome is more joyful.
Good ‘Till Cancelled (GTC) order
A Good ‘Till Cancelled (GTC) order remains active in the market until you cancel it. The broker will never cancel the order, and you are responsible for monitoring it.
Good for the day (GFD) order
A Good for the day (GFD) order only exists on the specific day. At the end of the trading day, the order is automatically removed if it has not been executed.
Once-cancels-the-other (OCO) order
The Once-cancels-the-other (OCO) order allows order B to be cancelled when order A is executed and vice versa. This can be useful when you are unsure of the direction of the price and want to take advantage of both potential breakthroughs downwards and upwards.
One-Triggers-the-Other (OTO) order
The One-Triggers-the-Other (OTO) order is an order in which the other orders are placed when this order is executed. For example, you can direct for a certain stop order to be placed after the trading position opens.
Conclusion: Which type of order is better?
For most investors, only the Market order and the Limit order are relevant. For long-term investors, the Market order is sufficient for most investors. However, if you are engaged in active speculation, the Limit order can give you more control over your investments.
Auteur

Over Alex Mostert
When I was 16, I secretly bought my first stock. Since that ‘proud moment’ I have been managing trading.info for over 10 years. It is my goal to educate people about financial freedom. After my studies business administration and psychology, I decided to put all my time in developing this website. Since I love to travel, I work from all over the world. Click here to read more about trading.info! Don’t hesitate to leave a comment under this article.
